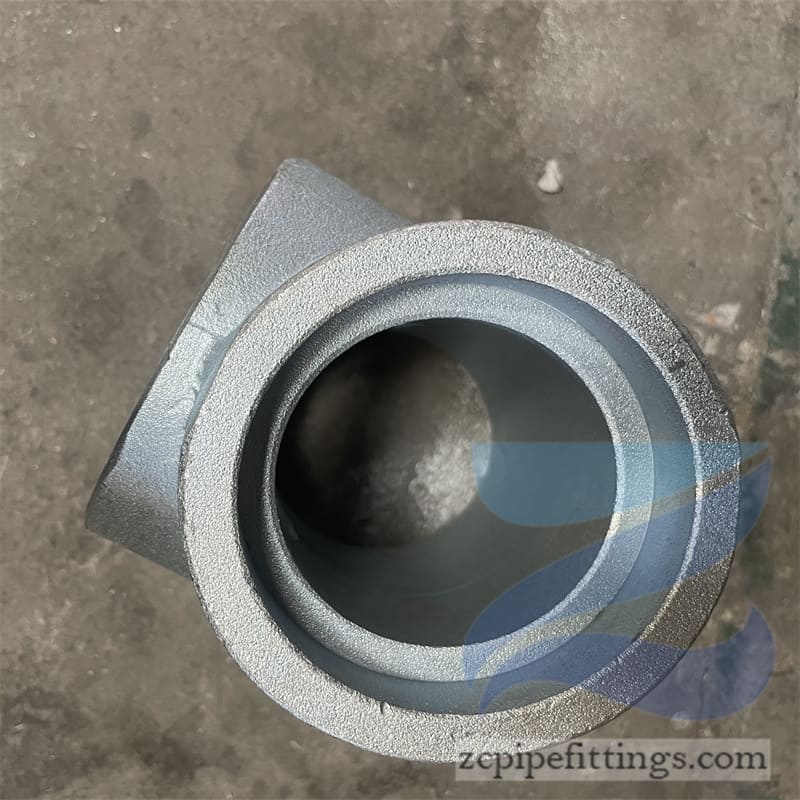
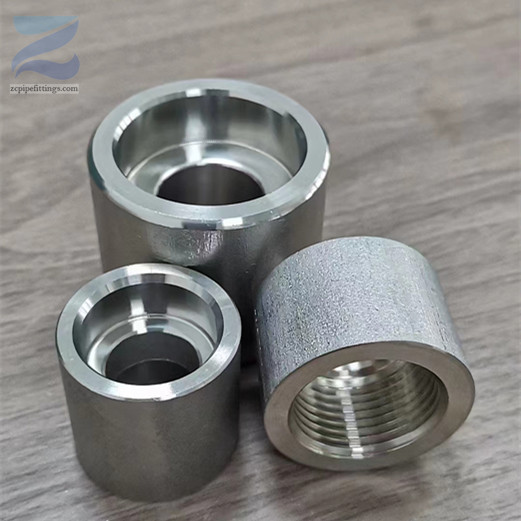
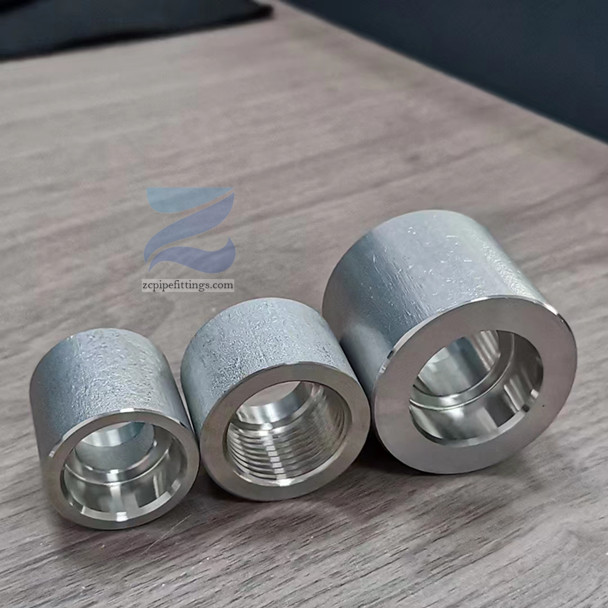
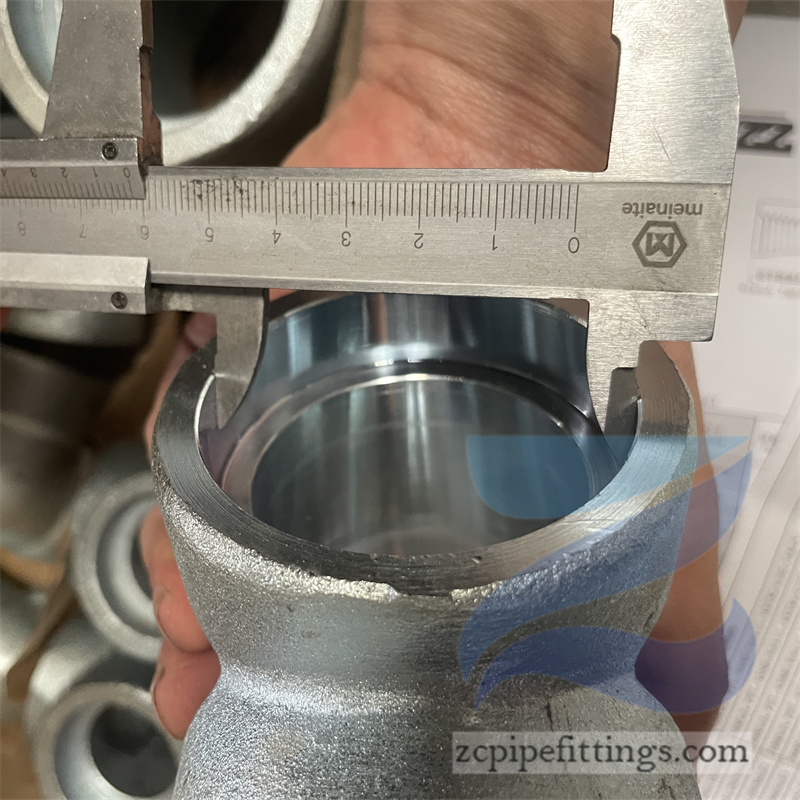
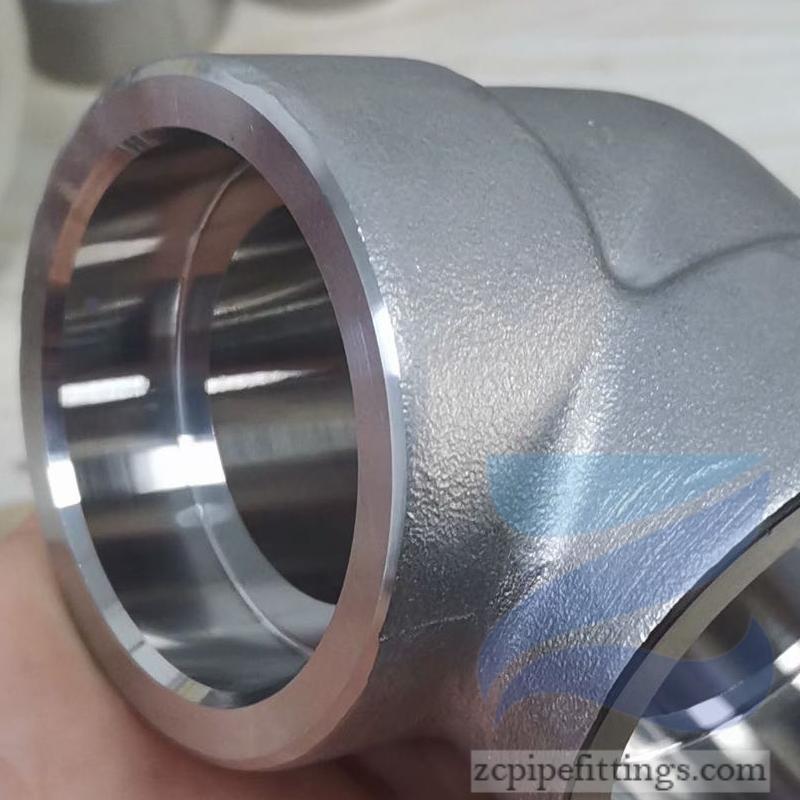
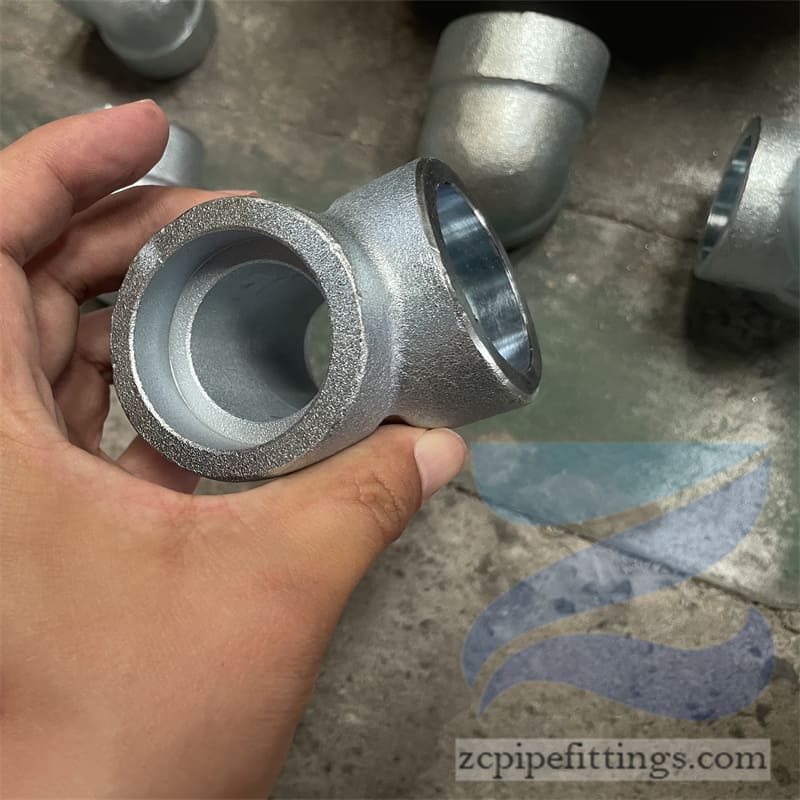
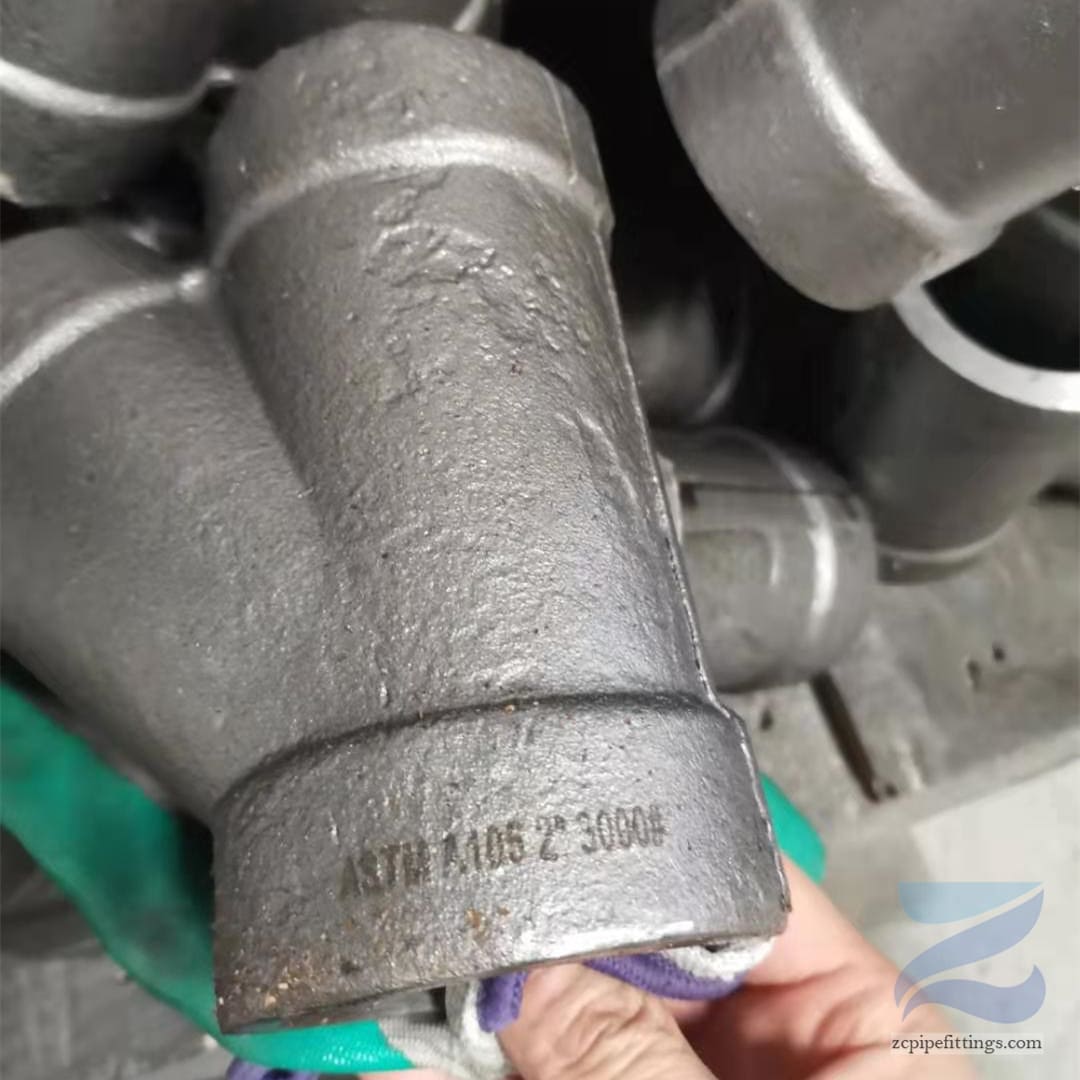
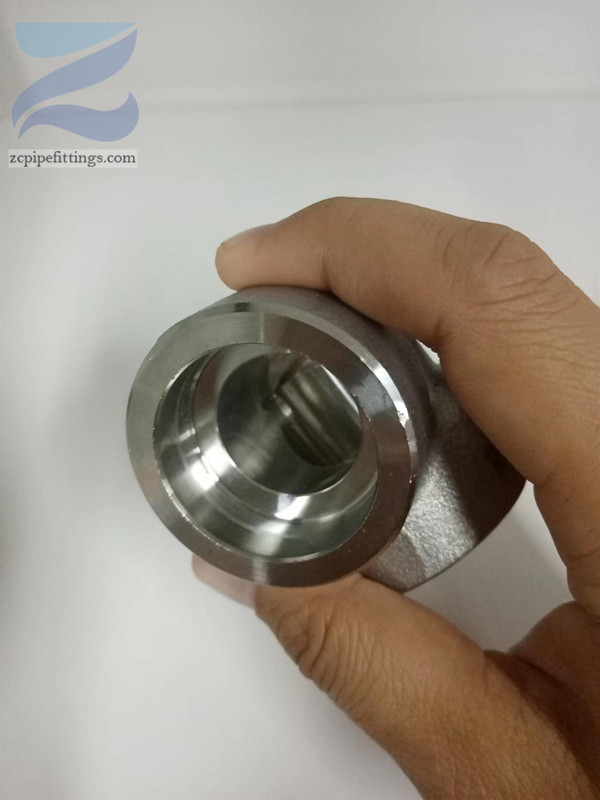
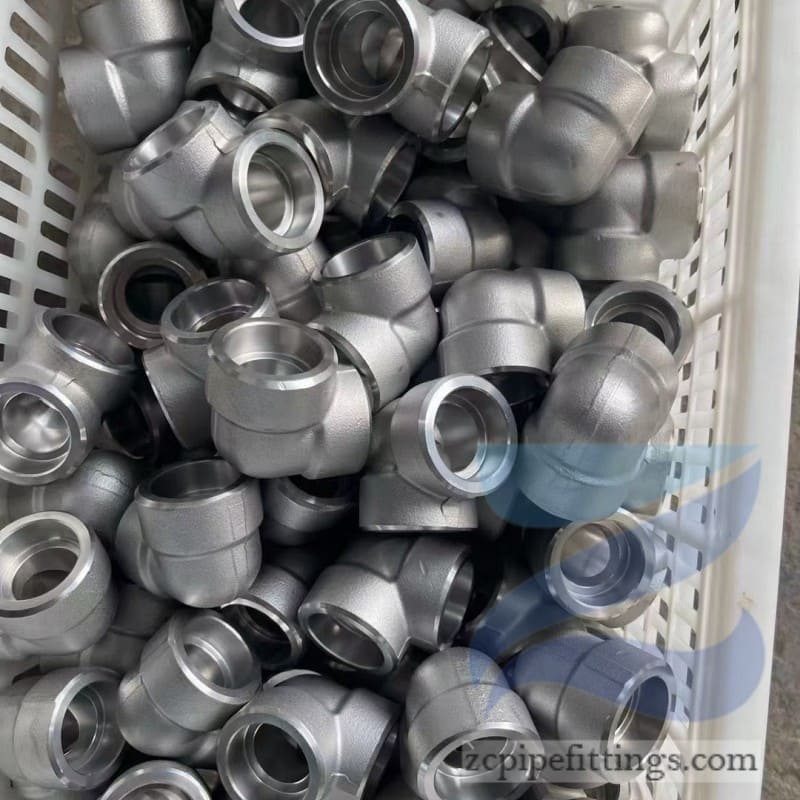
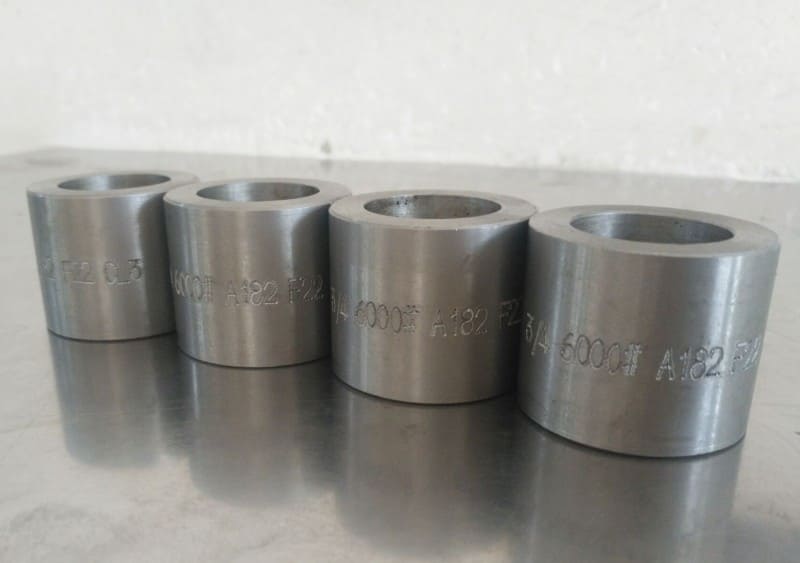
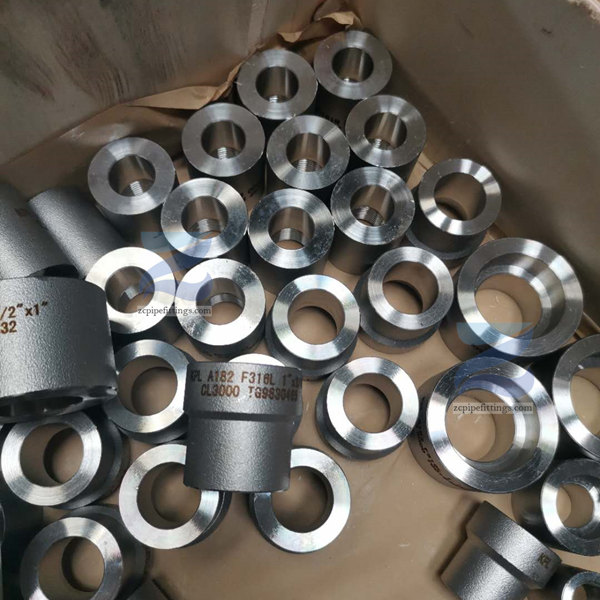
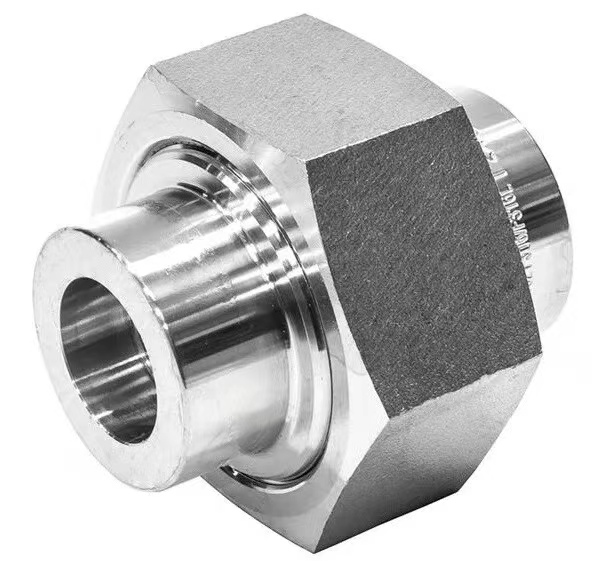
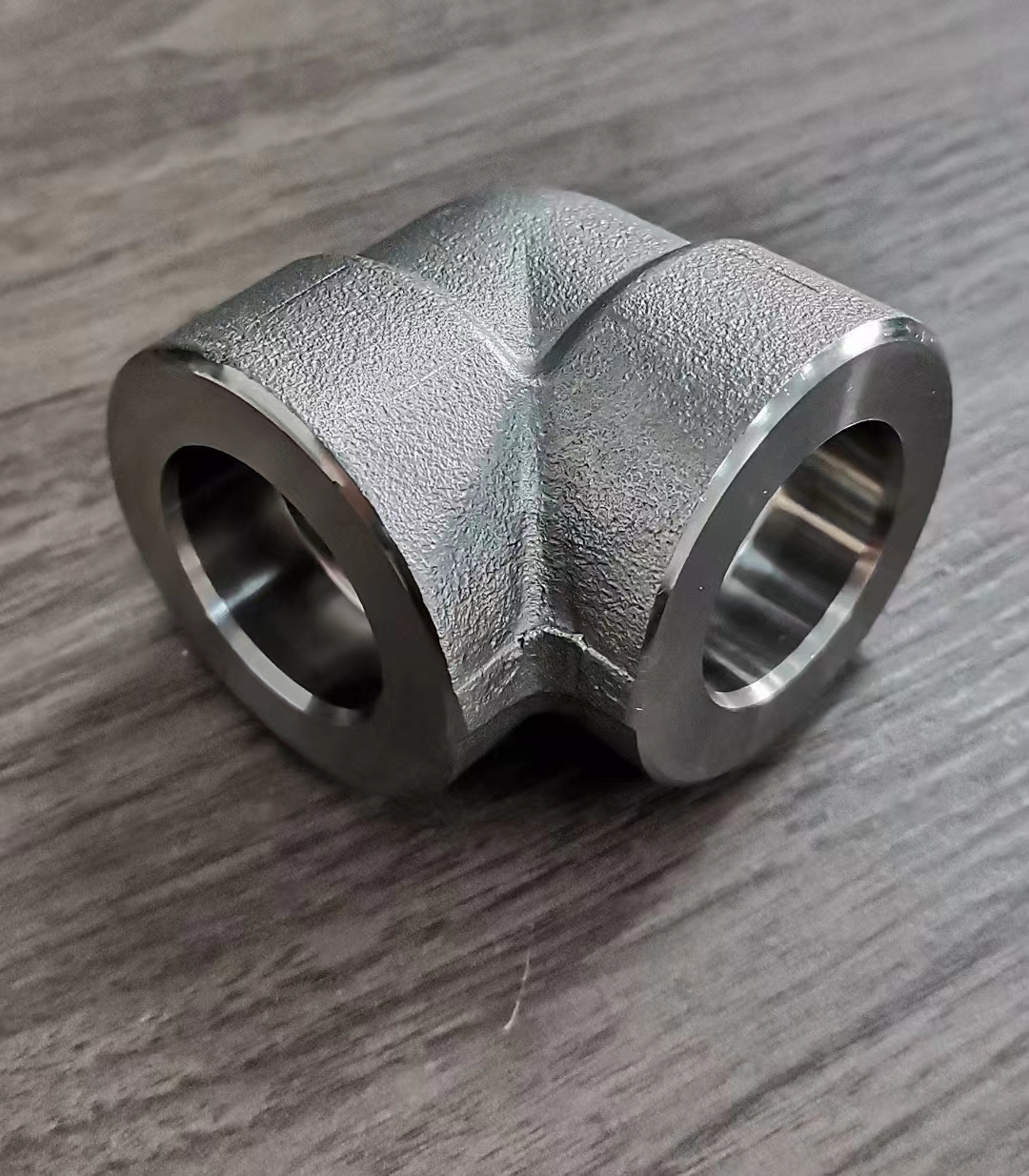
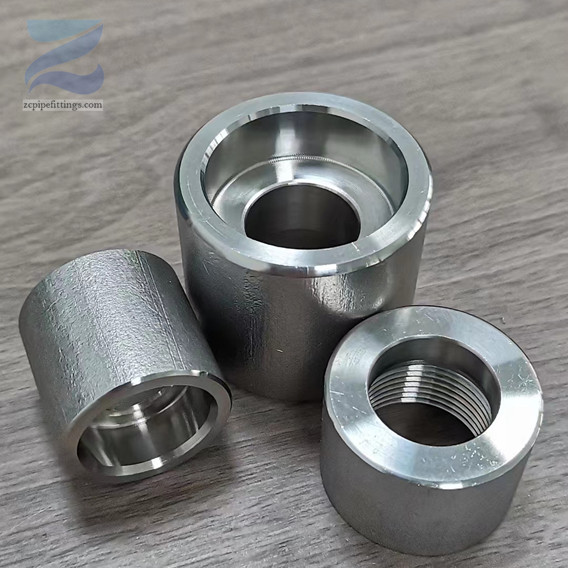
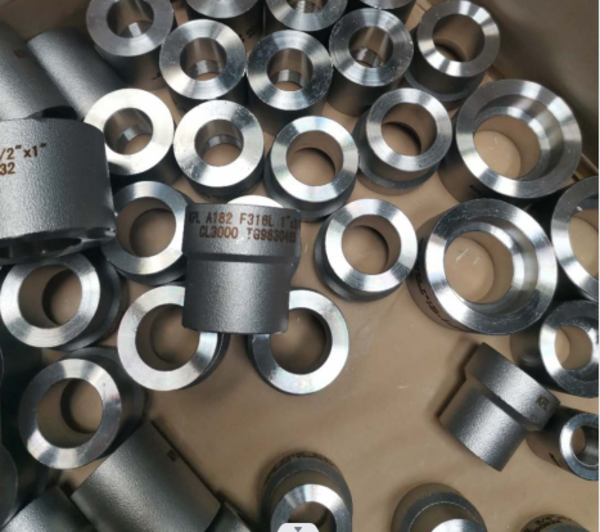
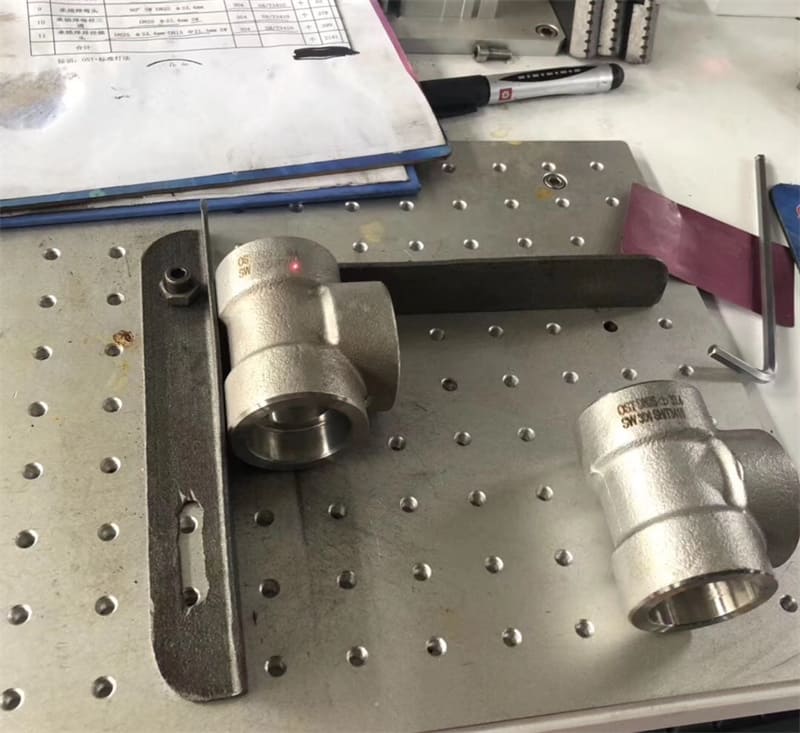
High Pressure Forged Steel Socket Weld Elbow
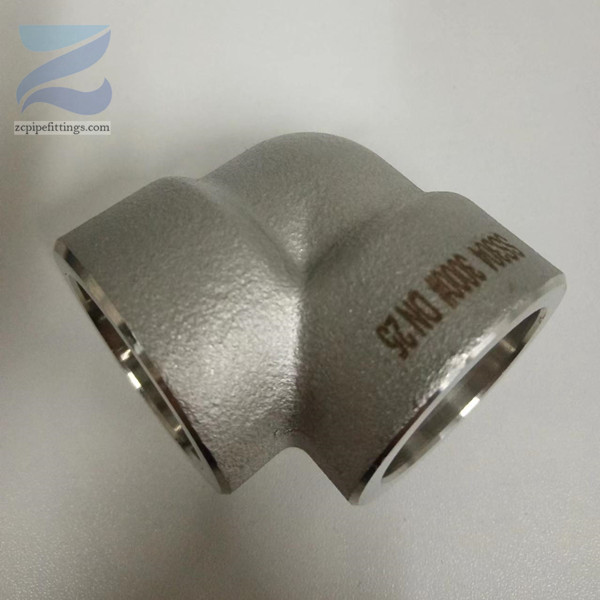
Available at90 degree and 45-degree angles, these fittings allow pipe runs to change direction. SW elbows can be either short radius or long radius designs as required.
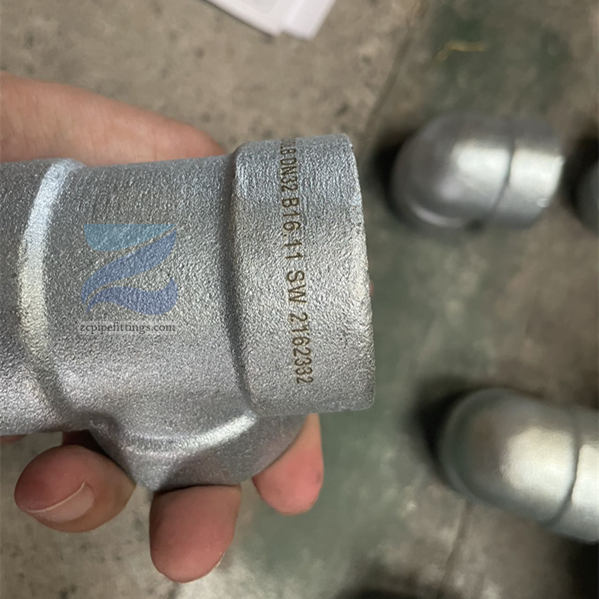
Socket welding (SW) is used for welding pipes and fittings including reducers, tees and elbows.
Socket weld pipe fittings are used to permanently join pipes that are inserted into a recess in the fitting, flange or valve. Once correctly inserted, fillet type sealing welds are applied to join the pipe to the fitting.
These fittings are commonly known as SW pipe fittings, with SW couplings, SW elbows and SW tees being examples of different types.
Socket welds can be used to change the direction of travel for pipe networks as well as join pipes at different angles and of different diameters.
The high leakage integrity and structural strength of socket welds allow them to be used for a range of piping network applications.
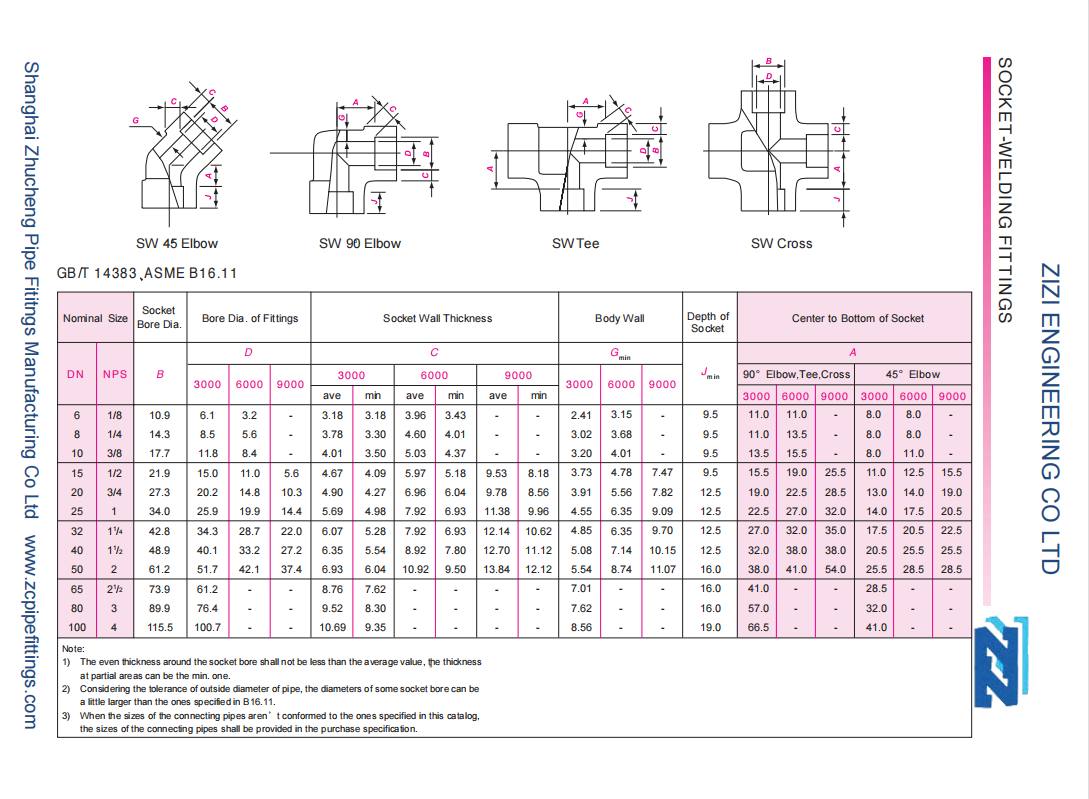
| Shape | Elbow, Tee, Cross, Coupling, Union, Cap, Reducing Insert, Sockolet |
| Size Range | 1/8″ – 4″ / DN6 – DN100 |
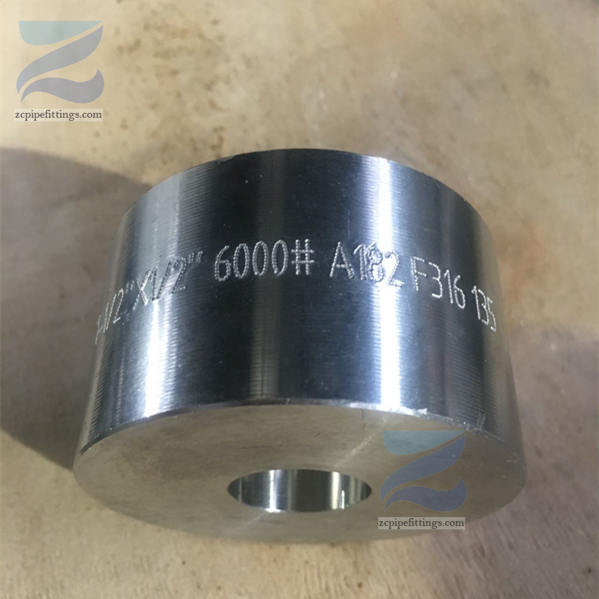
| Pressure Rating | Class 3000lbs, 6000lbs, 9000lbs |
| Standard | ASME B16.11, BS3799, EN 10241, MSS SP-83, MSS SP-97 |
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A105 / A105N, ASTM A350 LF2/LF3, ASTM A694 F42 / 46 / 56 / 60 / 65, P235GH, P265GH, P280GH, P355GH |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F11 / 12 / 5 / 9 / 91 / 92 / 22 |
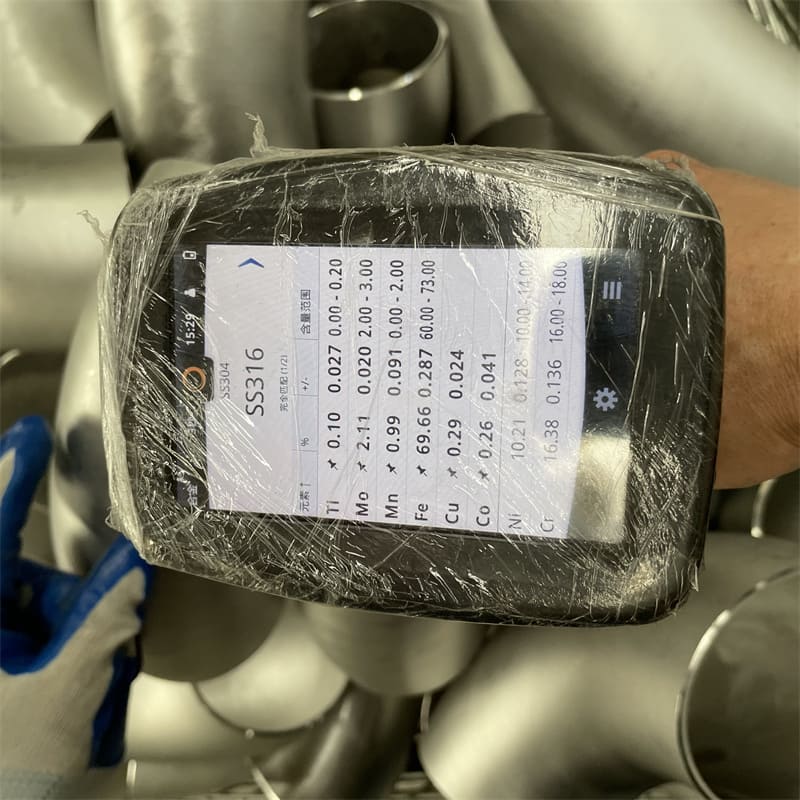
| Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F304/304L/304H, 316/316L, 321, 310S, 317, 347, 904L,1.4404, 1.4437. |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F51, F53, F44 |
How Socket Welding Works
Socket welding is named for the fittings into which the pipes are placed for welding. These fittings include recessed sockets into which the pipes are inserted before being welded into place.
When inserting the pipe into the socket it is important to leave a gap between the end of the pipe and the bottom of the socket. This gap prevents a stress failure from occurring when the heat from the welding process causes the pipes to expand against the socket. This gap can be manually measured and marked with a reference line on the pipe, or a permanent fitment tool can be inserted into the fitting to ensure the pipe does not bottom out into the socket. Once placed in position, the pipe is fixed in place by fillet welding where the pipe diameter meets the socket.
Socket welds create sealed, leak-proof, high pressure pipeline configurations for the transporting of liquids or gases. Unlike butt welding, socket welds don’t require any pre-weld machining, although the pipe ends should be clean in order to assure the integrity of the weld.
Uses and Applications
There are some applications that are not suitable for socket weld use, but the high pressure ratings associated with socket weld fittings mean that they are ideal for a wide range of other industrial applications.
SW pipe fittings can be used in pipelines to transport flammable, toxic or hazardous chemicals safely due to the lowered risk of leakage compared to other joining techniques.
Creating a leak-free permanent join, SW pipe fittings also allow for excellent flow characteristics. When manufactured to ASME and ASTM standard specifications, these fittings are shown to have met requirements for performance, including tolerances, pressure and temperature ratings, dimensions, materials and markings.
Socket weld pipe fittings are divided according to material type, such as alloy or carbon steel and stainless steel pipes. The different types of fitting lend themselves to different applications, whether couplings, reducers, reducing and regular socket weld tees, elbows, or flanges, with each available in different material types.































